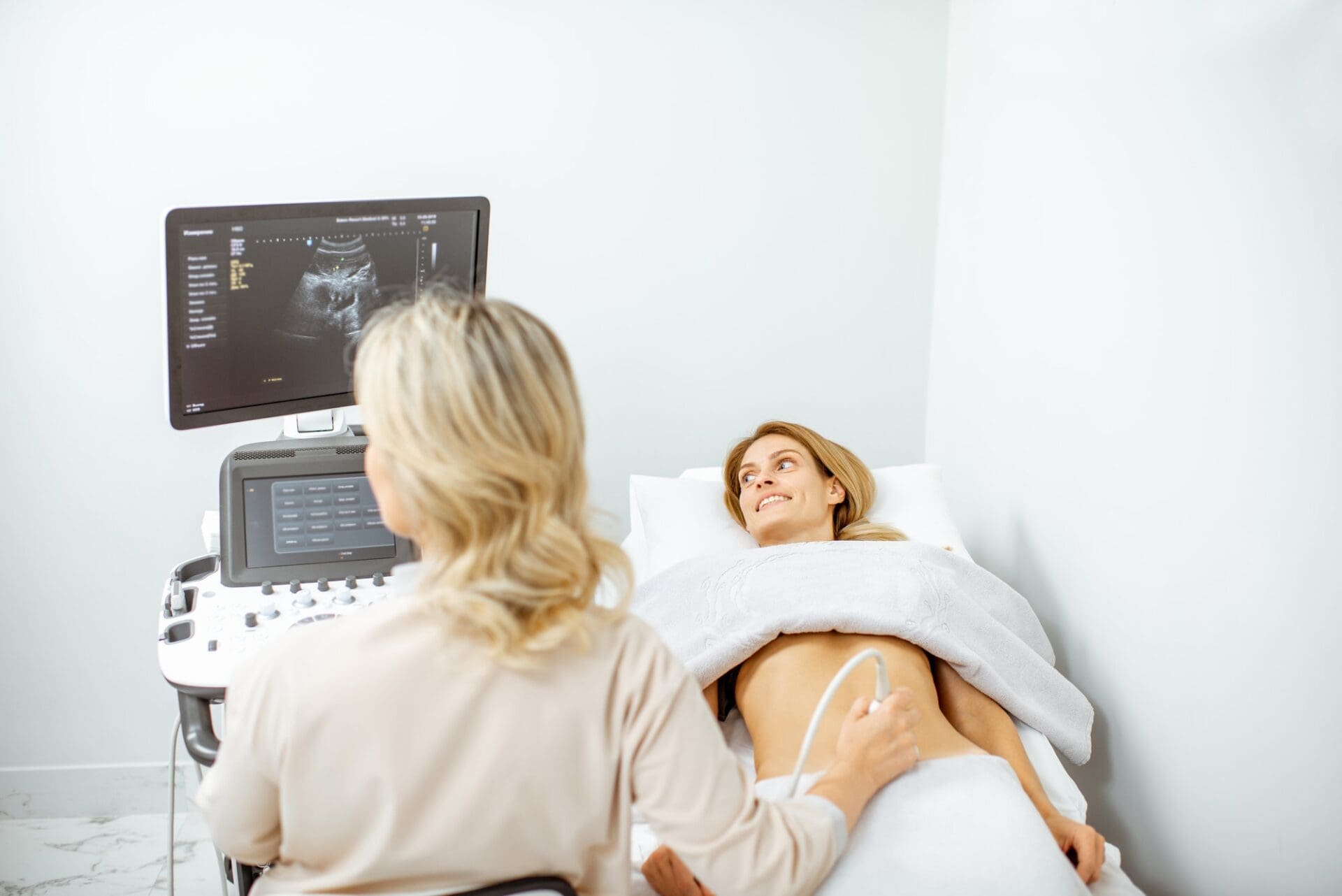
With the help of the abdominal ultrasound examination, one can get a picture of the situation of the inner organs with the help of high frequency sound waves that are not perceptible to the human ear.
It is a pain-free and quick way to examine problems of the liver, biliary channels, kidneys and pancreas, spleen, abdominal aorta and bladder. A kidney stone can just as well be diagnosed with the help of abdominal ultrasound, as a liver cyst. The organs of the uterine pelvis can also be seen, just as the uterus, the ovaries and the fallopian tubes. With the help of ultrasound, the size of the respective organ can be established, and anomalies, knots, enlargements and signs pointing to inflammations can be detected.
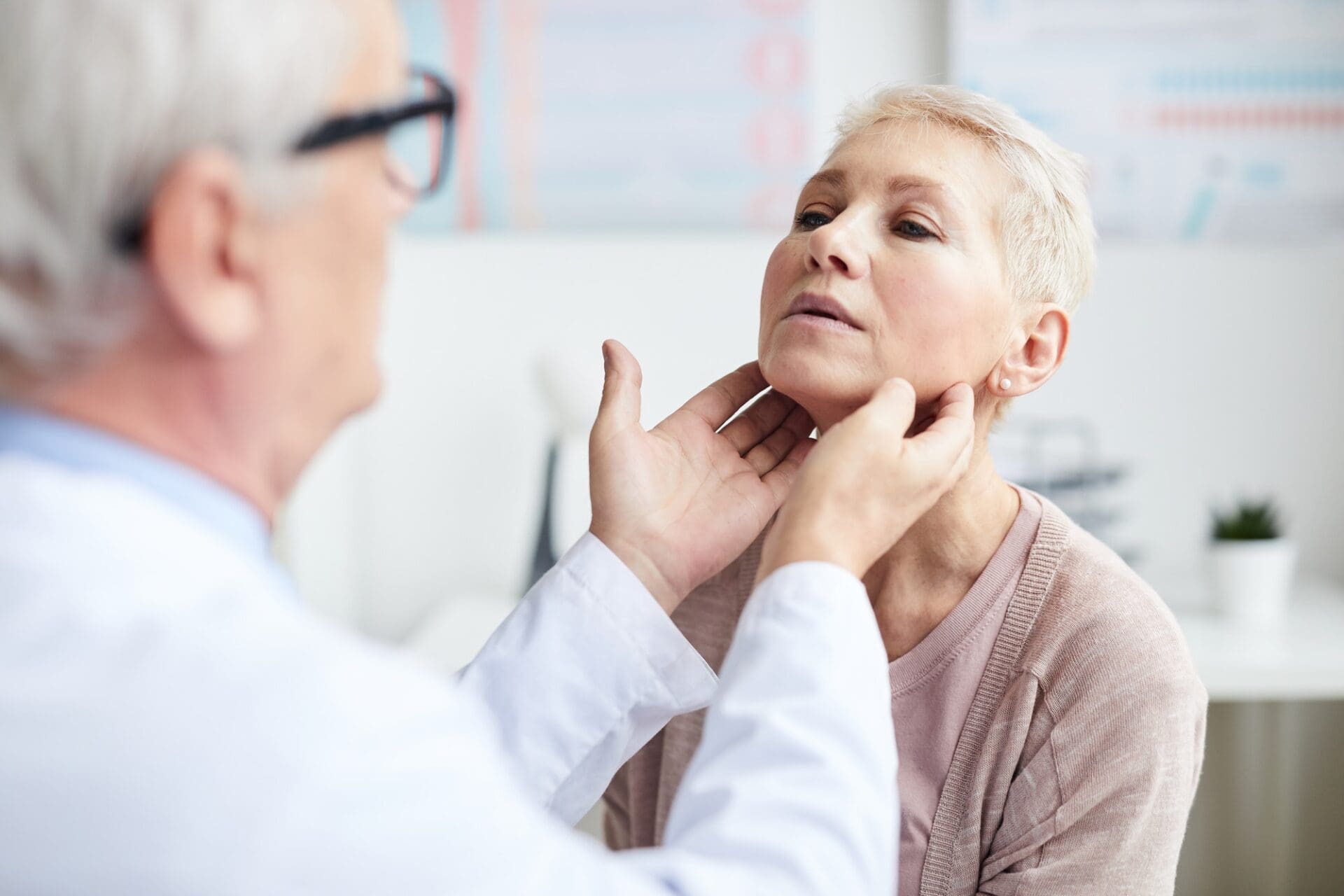
Diagnosing diseases of the thyroid gland normally necessitates several different examinations. The most common method applied first is the thyroid gland ultrasound, while the diagnosis must be fine-tuned by other examinations, as well.
The ultrasound examination helps to provide a precise diagnosis in the case of patients whose endocrinological lab results or isotope examinations pointed to the assumption of a thyroid gland disease. The ultrasound examination displays the size and structure of the thyroid gland and shows potential structural anomalies such as cysts or knots.
If necessary, tissue samples can be retrieved from these knots by biopsy, helping to choose the appropriate therapy. The accuracy of the examination does not amount to 100%. It can happen that certain abnormalities can only be discovered after several examinations.
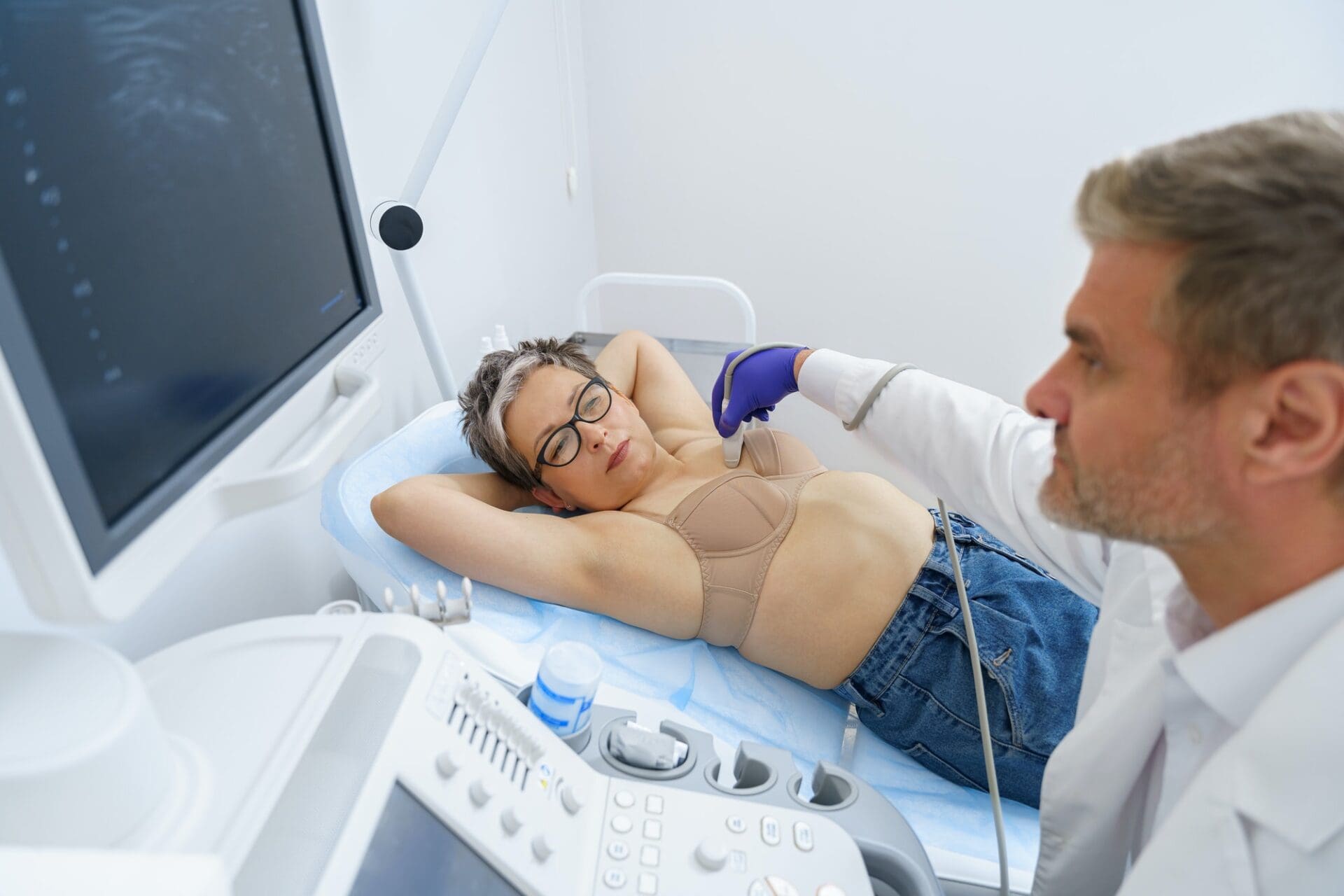
It can happen that you sense a knot while inspecting your breasts at home, or that a change is detected during the gynaecological examination. It is important to consult your doctor and register for an ultrasound examination in case you sensed any anomaly or change when inspecting yourself at home. During the ultrasound examination, we look at the glandular tissue, armpits, lymph nodes, the area around the breastbones, and the areas below and above the collarbone. This ultrasound examination is done when controlling a disease known to the doctor and patient, when controlling a cancer, and to check the state of health during a screening examination.
Above the age of 35 the ultrasound examination is not sufficient for a precise diagnosis, but is done as a complementary exam to the mammography screening. The breast ultrasound is non-invasive, secure, pain free and does not affect the sugar load in the blood. Breast ultrasounds allow to detect anomalies at an early stage that can still be healed! Preventive breast ultrasound is advised once a year in the case of women above the age of 16, and in case you are taking contraceptives or hormonal medicines or have a breast implant, or if ordered by your doctor.
Copyright © 2024 Villa Medicina All rights reserved – made by digitalhero